7. PostREISE¶
This tutorial focuses on the analysis and plotting of scenario output data. PostREISE is an open source package written in Python that is available on GitHub.
Note that analysis and plotting tools in this package rely extensively on our scenario framework presented in the PowerSimData tutorial.
7.1. Scenario used¶
You will find below a short description of the scenarios that will be used across this tutorial:
Scenario 403 was designed to represent the Eastern interconnect in the year 2020.
Scenario 3287 was designed to represent the entire U.S. in the year 2030, where there is a large increase in transmission capacity (but no increase across interconnection seams) and carbon-free energy represents approximately 70% of total generation over the course of the year.
Scenario 2497 was designed to represent the Western interconnect in the year 2030, where 90% of the total energy could come from carbon-free sources, but the transmission network has not been upgraded to accommodate these new clean generation sources. Of this 90% potential, 10% could come from nuclear.
Scenario 1171 was designed to represent the Western interconnect in the year 2030, with all states meeting their clean energy goals (with ‘collaboration’ via imports and exports across state lines) and there are 4 GW of energy storage capacity.
Scenario 3101 was designed to represent the Western interconnect in the year 2030, where 90% of the total energy does come from carbon-free sources, enabled by upgrades in the transmission network to accommodate these new clean generation sources. Of this 90% potential, 10% comes from nuclear.
7.2. Analysis of Scenario Data¶
Several categories of analysis focusing on:
transmission congestion/utilization
generation and generator capacity
emission (\(\rm{CO}_2\), \(\rm{NO}_x\) and \(\rm{SO}_2\)) from thermal generators
curtailment of renewable generators
can be conducted with the PostREISE package.
You will find below some code snippets that will help you use these analysis tools for each category. Information on the input and returned parameter(s) of the analysis functions can be found on this website. Use the Module Index to locate a module and access the documentation along with the source code of the objects therein.
7.2.1. Transmission¶
calculate the hourly congestion surplus
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.transmission.congestion import calculate_congestion_surplus scenario = Scenario(403) congestion_surplus = calculate_congestion_surplus(scenario)
get the hourly utilization level (in [0, 1]) of the branches, i.e., the extent to which the transmission path is used
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.transmission.utilization import get_utilization scenario = Scenario(403) grid = scenario.get_grid() pf = scenario.get_pf() utilization = get_utilization(grid.branch, pf)
obtain utilization/congestion statistics for each line
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.transmission.utilization import generate_cong_stats scenario = Scenario(403) grid = scenario.get_grid() pf = scenario.get_pf() congestion_stats = generate_cong_stats(pf, grid.branch)
The columns of the returned table are:
capacity: the capacity of the linebranch_device_type: the type of lineper_util1,per_util2andper_util3: fraction of hours the line is used above threshold 1, 2 and 3. Default value for threshold are 0.75, 0.9 and 0.99, respectivelybind: number of hours the line is used at full capacityrisk: total power flowing on the line for hours used above threshold 1 (0.75 by default)uflag1,uflag2anduflag3: threshold forper_util1,per_util2andper_util3. Default values for threshold are 0.5, 0.2 and 0.05, respectivelysumflag: total number of flags (in [0, 3])dist: the length of the line
7.2.2. Generator Capacity and Generation¶
identify hours for which generators are at minimum power, maximum power and have binding ramp constraints
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.binding import ( pmax_constraints, pmin_constraints, ramp_constraints, ) scenario = Scenario(3287) binding_pmin = pmin_constraints(scenario) binding_pmax = pmax_constraints(scenario) binding_ramp = ramp_constraints(scenario)
calculate the net load duration curve, i.e., the capacity value of a class of resources by comparing the mean of the top N hour of absolute demand to the mean of the top N hours of net demand
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.capacity import calculate_NLDC scenario = Scenario(3287) nldc = calculate_NLDC(scenario, {"ng", "coal"})
calculate the capacity value of a class of resources by averaging the power generated in the top N hours of net load peak
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.capacity import calculate_net_load_peak scenario = Scenario(3287) nlp = calculate_net_load_peak(scenario, {"nuclear", "hydro"}, hours=50)
get the total nameplate capacity for generator type(s) in an area
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.capacity import get_capacity_by_resources scenario = Scenario(2497) resources_capacity = get_capacity_by_resources(scenario, "CA", {"solar", "wind"})
get total storage nameplate capacity in an area
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.capacity import get_storage_capacity scenario = Scenario(1171) storage_capacity = get_storage_capacity(scenario, "CA")
get the total nameplate capacity for each generator type and load zone combination
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.capacity import sum_capacity_by_type_zone scenario = Scenario(2497) capacity = sum_capacity_by_type_zone(scenario)
get the hourly capacity factor of each generator fueled by resource(s) in an area
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.capacity import get_capacity_factor_time_series scenario = Scenario(3287) capacity = get_capacity_factor_time_series( scenario, "Texas", {"solar", "wind"}, area_type= "interconnect" )
get the total generation for each generator type and load zone combination
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.summarize import sum_generation_by_type_zone scenario = Scenario(3101) generation = sum_generation_by_type_zone(scenario)
get the total generation for each generator type and state combination, adding totals for the interconnects and for all states
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.summarize import sum_generation_by_state scenario = Scenario(3101) generation = sum_generation_by_state(scenario)
get the total historical generation for each generator type and state combination, adding totals for interconnects and for all states
import inspect import os import pandas as pd import postreise from postreise.analyze.generation.summarize import summarize_hist_gen data = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(inspect.getfile(postreise)), "data") hist_gen = pd.read_csv( os.path.join(data, "2016_Historical_USA_TAMU_Generation_GWh.csv"), index_col=0 ).T historical_generation = summarize_hist_gen(hist_gen, hist_gen.columns.to_list())
get hourly total generation for generator type(s) in an area
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.summarize import ( get_generation_time_series_by_resources, ) scenario = Scenario(3287) generation = get_generation_time_series_by_resources( scenario, "Western", {"solar", "wind"} )
get hourly total storage power generation in an area
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.summarize import get_storage_time_series scenario = Scenario(1171) generation = get_storage_time_series(scenario, "Western")
7.2.3. Emission¶
calculate hourly emissions for each generator
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.emissions import generate_emissions_stats scenario = Scenario(403) emission = generate_emissions_stats(scenario, pollutant="carbon", method="simple")
Different methods can be used to infer the carbon emission:
‘simple’ uses a fixed ratio of \(\rm{CO}_2\) to MWh
‘always-on’ uses generator heat-rate curves including non-zero intercepts
‘decommit’ uses generator heat-rate curves but de-commits generators if off
Only the ‘simple’ method can be used to infer emission of \(\rm{NO}_x\) or \(\rm{SO}_2\).
Pollutant options:
carbon= carbon dioxide (\(\rm{CO}_2\))nox= nitrogen oxides (\(\rm{NO}_x\))so2= sulfur dioxide (\(\rm{SO}_2\))
calculate total emissions by generator type and bus
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.emissions import ( generate_emissions_stats, summarize_emissions_by_bus, ) scenario = Scenario(403) grid = scenario.get_grid() emission = generate_emissions_stats(scenario, pollutant="carbon", method="simple") emission_by_resources_and_bus = summarize_emissions_by_bus(emission, grid)
calculate individual generator costs at given power output
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.emissions import calculate_costs scenario = Scenario(403) costs = calculate_costs(scenario)
7.2.4. Curtailment¶
calculate hourly curtailment for each renewable generator
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import ( calculate_curtailment_time_series, ) scenario = Scenario(403) curtailment = calculate_curtailment_time_series(scenario)
calculate hourly curtailment by generator type(s)
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import ( calculate_curtailment_time_series_by_resources, ) scenario = Scenario(403) curtailment = calculate_curtailment_time_series_by_resources( scenario, {"wind", "solar"} )
calculate hourly curtailment by area(s)
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import ( calculate_curtailment_time_series_by_areas, ) scenario = Scenario(3287) curtailment = calculate_curtailment_time_series_by_areas( scenario, {"state": ["CA", "WA", "OR", "NV", "UT"]} )
calculate scenario-long average curtailment fraction for a set of generator type(s)
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import ( calculate_curtailment_percentage_by_resources, ) scenario = Scenario(3287) curtailment = calculate_curtailment_percentage_by_resources( scenario, {"wind", "solar"} )
calculate hourly curtailment of each generator located in area(s) and fueled by resource(s)
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import ( calculate_curtailment_time_series_by_areas_and_resources, ) scenario = Scenario(3287) curtailment = calculate_curtailment_time_series_by_areas_and_resources( scenario, areas={"state": ["Maine", "CA", "TX"]})
calculate hourly curtailment of each generator fueled by resources and located in area(s).
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import ( calculate_curtailment_time_series_by_resources_and_areas, ) scenario = Scenario(3287) curtailment = calculate_curtailment_time_series_by_resources_and_areas( scenario, areas={"state": ["Maine", "CA", "TX"]})
calculate total curtailment by bus
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import summarize_curtailment_by_bus scenario = Scenario(403) curtailment = summarize_curtailment_by_bus(scenario)
calculate total curtailment by location
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import ( summarize_curtailment_by_location, ) scenario = Scenario(2497) curtailment = summarize_curtailment_by_location(scenario)
get hourly curtailment for each available renewable resource(s) in area.
from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.analyze.generation.curtailment import get_curtailment_time_series scenario = Scenario(2497) curtailment = get_curtailment_time_series(scenario, "WA")
7.3. Plotting Scenario Data¶
The plotting functions use the analysis modules to process data. We have a demo folder that encloses numerous notebooks that we hope will help you analyze/display your scenario data.
7.3.1. Single Scenario¶
7.3.1.1. Transmission¶
get a power flow snapshot (notebook)
import pandas as pd from bokeh.io import show from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.plot.plot_powerflow_snapshot import plot_powerflow_snapshot scenario = Scenario(3287) grid = scenario.get_grid() pf_map = plot_powerflow_snapshot( scenario, pd.Timestamp(2016, 11, 2, 22), legend_font_size=20 ) show(pf_map)
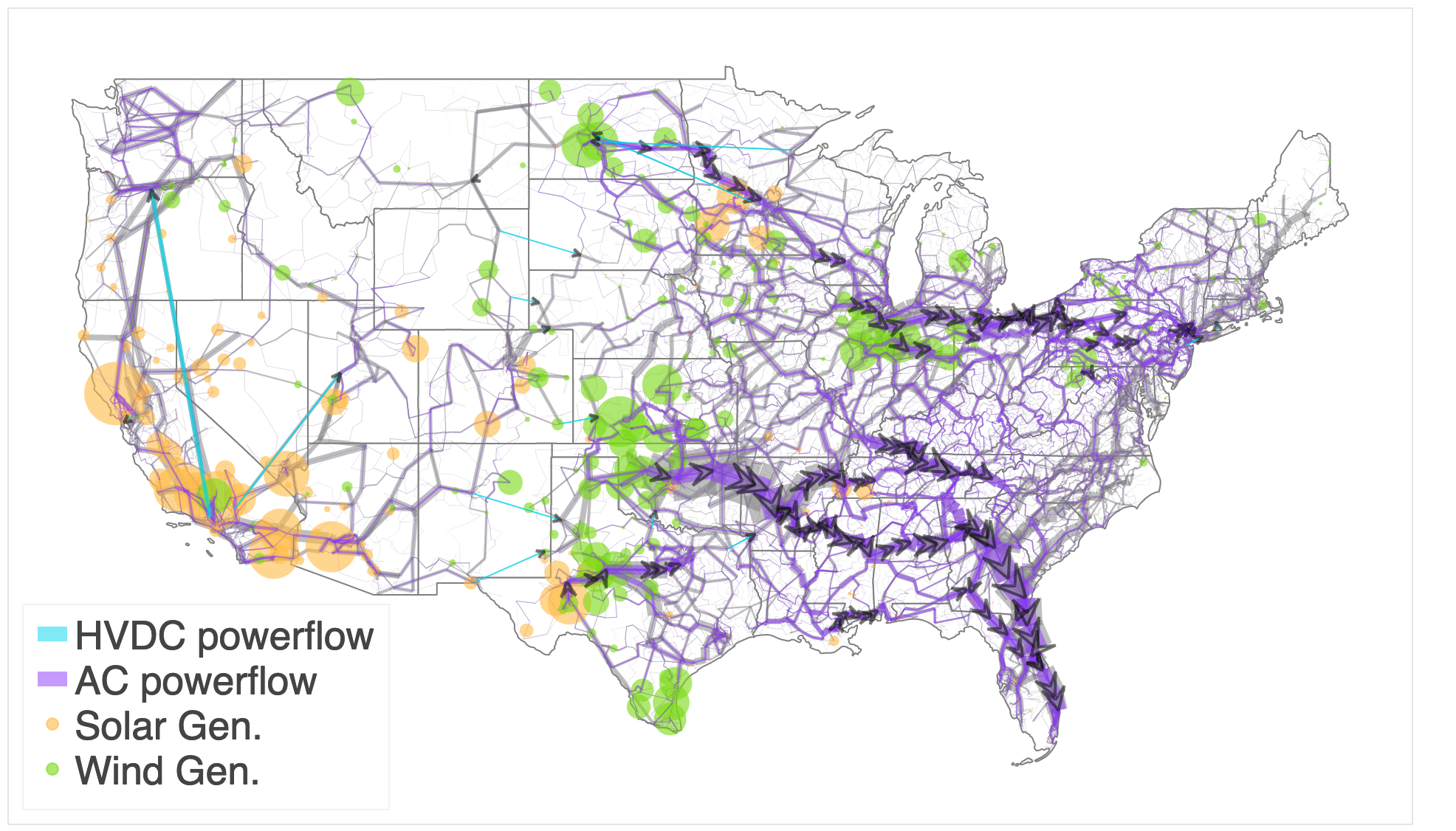
get utilization map (notebook)
from bokeh.io import show from powersimdata import Scenario from postreise.plot.plot_utilization_map import map_utilization scenario = Scenario("3287") util_map = map_utilization(scenario, state_borders_kwargs={"background_map": False}) show(util_map)
Bokeh Plot